22.04.2024 - 19.05.2024 (Week 1 - Week 4)
Gunn Joey / 0366122
Video and Sound Production / Bachelor of Design (Hons) in Creative Media
Exercises
TABLE OF CONTENTS
2. Week 1 Task
- Editing Exercises
- Quiz Result
3. Week 2 Task
- Framing & Storyboard Exercises
- Shooting Exercise
- Editing: Lalin
- Asynchronous Class Materials Questions
- Quiz Result
4. Week 3 Task
- Asynchronous Class Materials Questions
- Quiz Result
5. Week 4 Task
- Asynchronous Class Materials Questions
- Quiz Result
6. Week 7 Task
MODULE INFORMATION BOOKLET
WEEK 1 TASK
Editing Exercises
After the module briefing is given by Mr Martin, our first task of the first
week is to import footage into Premiere Pro and arrange shots on timeline with
proper order. There are two editing exercises. Class editing exercises and
independent learning exercise.
1. Mints - class editing exercise
Figure 1.1 Mints
2. Doritos - independent learning exercise
Figure 1.2 Doritos
Asynchronous Class Materials
Reflection:
Camera shots are sufficient aspect of filmmaking and video productions, because by
combining different types of shot size, camera angles and composition.
They are all elements visual storytelling used in film, television and
other visual media. Filmmakers are able to bring out specific emotions,
ideas and movement for each scene as different shot sizes can create
different emotional effects.There are many different camera shots such as medium shot, medium
closeup, medium full shot, closeup, extreme closeup...... I learned that
choosing the right shot for each moment to film character expressing their
emotion helps to bring out the story's message and seek audience's
attention.
Rather than shooting the subject, compose an image with framing details
is also crucial. Moreover, filmmakers also focus on deciding the angle of shot, camera movements to
direct attention around different parts of the scene. I learned that
focus pull is passive and rack focus is aggressive. Different
position of the camera that related to the subject can affect audience's
perception. Camera angles lead audience's attention on the cinematic
effect and emotions. Furthermore, shot composition refers to the
arrangement of visual elements within a shot or frame. It can be used to
guide the viewer's eye and convey meaning or emotion.
Quiz Result:
Figure 1.4 Quiz result
[back to top]
WEEK 2 TASK
Framing & Storyboard Exercises
Mr Martin told us to watch a video that is provided in the Google Slides.
The video is named "Christmas Advert" by John Lewis. After watching
the video, we learned different shot sizes. Mr Martin also asked us to
answer and name different shot size for each shots in the video.
1. John Lewis Christmas Advert 2014
Medium Shot
|
|
Medium Shot
Figure 2.1.3 shot size
Wide Shot
Figure 2.1.4 shot size
Wide Shot
Figure 2.1.5 shot size
Medium Close-up Shot (MCU)
Figure 2.1.6 shot size
Medium Shot
Figure 2.1.7 shot size
Medium Shot
Figure 2.1.8 shot size
Medium Shot
Figure 2.1.9 shot size
Over the Shoulder Shot:
The over-shoulder shot shows the subject from behind the shoulder of another person. It may not always feature the 'shoulder' in the foreground. Instead, the aim is to present the point of view from the foreground character's perspective.

Figure 2.1.10 Over the shoulder shot
- Why the bottom shot is not an 0.S shot?
The bottom shot is not an over-shoulder shot as the scene does not present the point of view from the foreground character's perspective. Moreover, a O.S shot will suggest a connection between the characters in the scene. This scene does not have a connection between the character in the scene.
2. "Unsung Hero", Thai Life Insurance Ad
Figure 2.2.1 Unsung Hero
Mr Martin told us to watch this video and name different shot size
for each shots in the video.
Medium Close-up Shot
Figure 2.2.2 shot size
Close-up Shot
Figure 2.2.3 shot size
Close-up Shot
Figure 2.2.4 shot size
Medium Close-up Shot
Figure 2.2.5 shot size
Medium Wide Shot
Figure 2.2.6 shot size
Medium Wide Shot
Figure 2.2.7 shot size
Extreme Wide Shot
Figure 2.2.8 shot size
Close-up Shot
Figure 2.2.9 shot size
Medium Wide Shot
Figure 2.2.10 shot size
Medium Wide Shot
Figure 2.2.11 shot size
Medium Close-up Shot
Figure 2.2.12 shot size
Medium Shot
Figure 2.2.13 shot size
Medium Wide Shot
Figure 2.2.14 shot size
Medium Close-up Shot
Figure 2.2.15 shot size
Medium Shot
Figure 2.2.16 shot size
Wide Shot
Figure 2.2.17 shot size
Depth Of Field
- What are the foreground, midground, and background in composition? Provide an image for explanation.
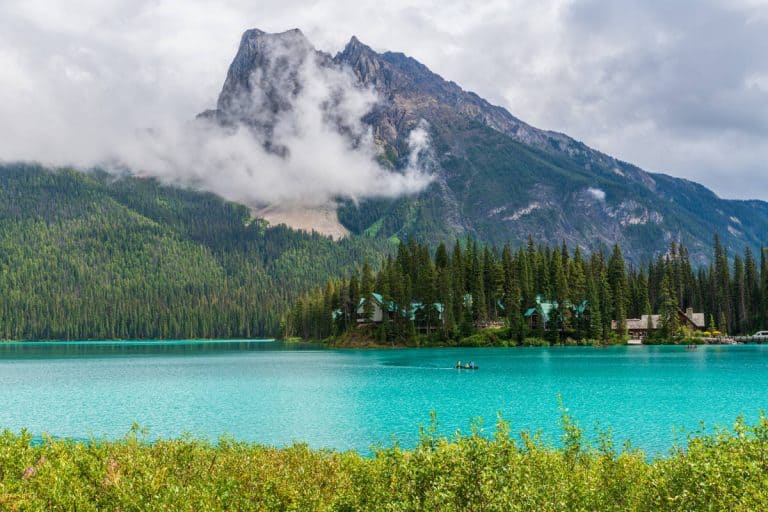

Figure 2.3.1 depth of field
The element of the photo closest to viewer makes up the foreground. The furthest element away from viewer is the background, while the mid ground makes up the area in
between.
- What is depth of field?
- What is deep depth of field? Provide an image for explanation.
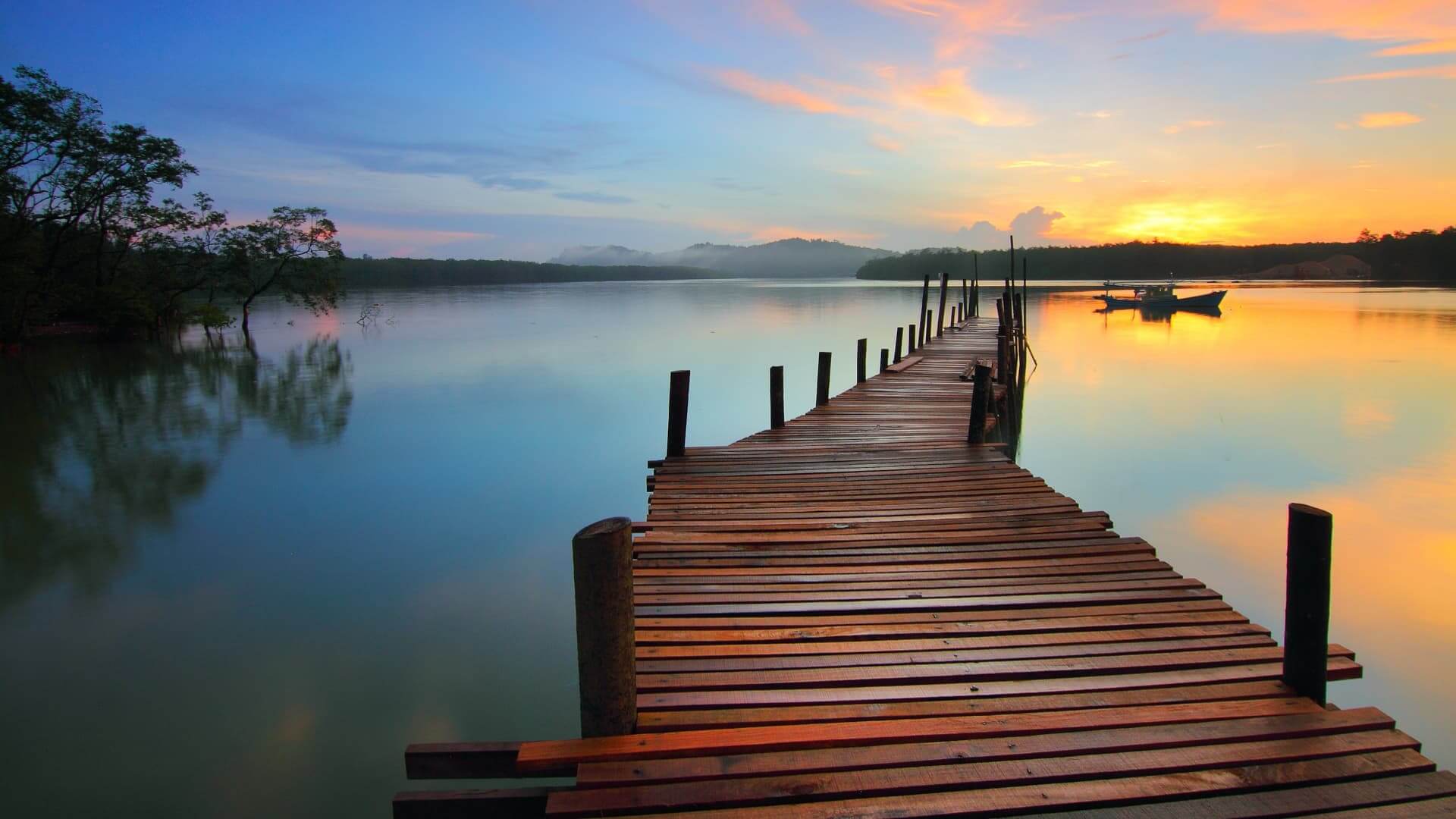

Figure 2.3.2 depth of field
Deep depth of field means a larger area in focus as it keeps more
of the image sharp and clear. Everything in frame is in focus but
sometimes this isn't what viewer is looking for.
- What is shallow depth of field? Provide an image for explanation.
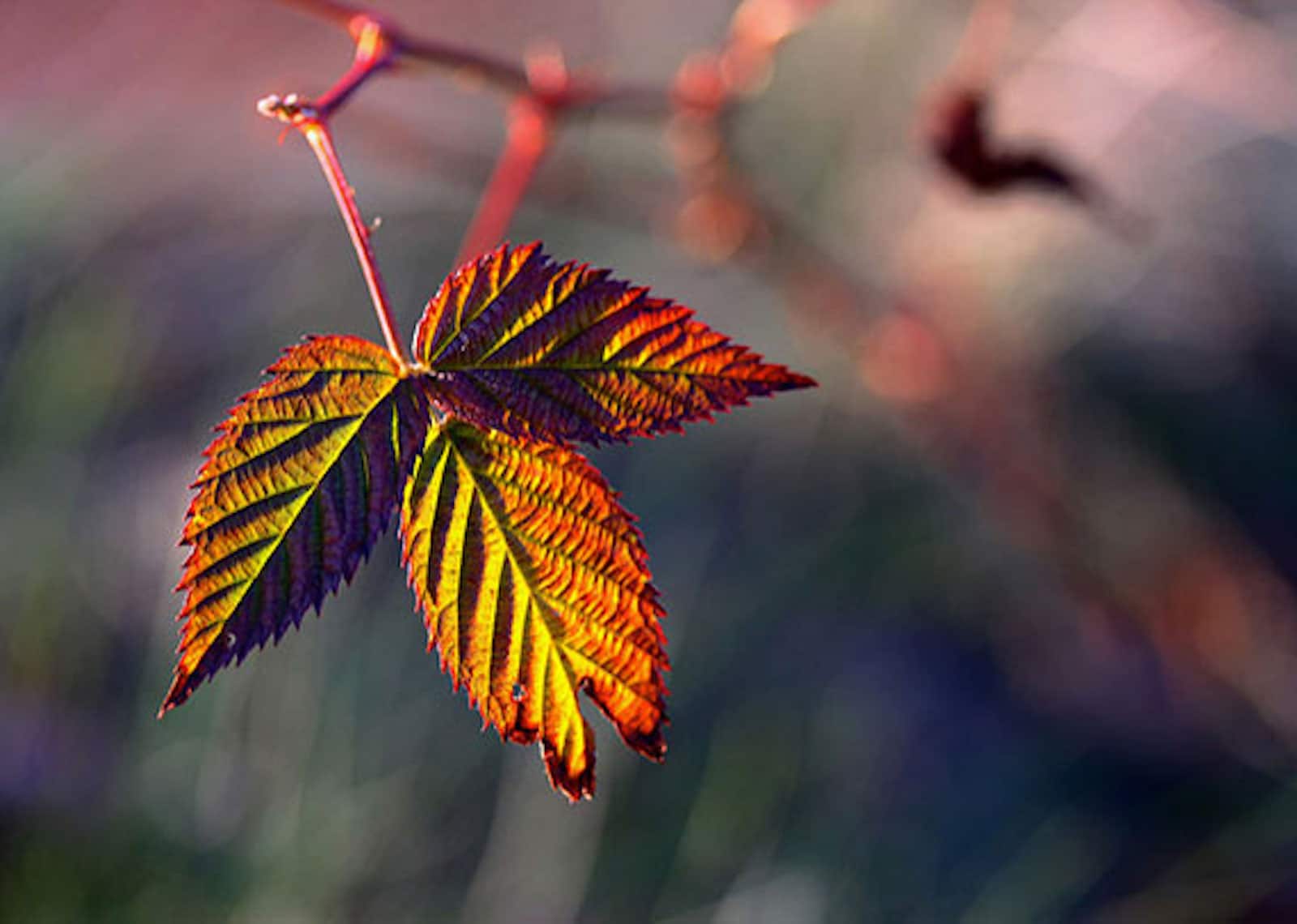

Figure 2.3.3 depth of field
A shallow depth of field refers to as narrow or even thin depth of field. The background is blurred while only the object stays in focus. Shallow depth of field works well in portrait photos.
Screen Direction
- What is 180 degree rule (static screen direction)?
180 degree rule (static screen direction) means two characters or more in a scene should always have the same left or right relationship with each other. This rule is a filmmaking technique that keeps the camera on one
side of an imaginary line that separates two characters.
In movies and animation, it helps viewers follow the action smoothly.
- What is continuity in cinematography?
Continuity in cinematography means keeping everything in a movie consistent to make the story easy to follow. This includes matching character movements between shots, keeping objects in the same place and condition, ensuring characters wear the same clothes in a scene, maintaining the same lighting throughout scenes, and keeping locations and their layout consistent.
- Watch the video below. Does it adhere to the 180 degree rule?
Figure 2.4 screen direction
Yes, the video adhere to the 180 degree rule as the characters in the scene have their own relationship.
- What is dynamic screen direction?
Dynamic screen direction refers to the use of camera movement in the scene to guide viewers' attention and convey action, emotion and narrative progression. This includes tracking shots that follow a character or complex choreography of actors and camera to create visually captivating sequences.
Shooting Exercise: Framing
Figure 2.5.1 Shooting Exercise
Reminder:
- Shoot landscape format video, 5 seconds per shot.
- Shoot wide shot with wide angle.
- The rest ZOOM IN to get soft background.
- Refer to the examples provided or google references for GOOD composition.
- Avoid overexposed or underexposed (too bright or too dark).
- Do the shooting during day time.
- Edit with CAPTION (Mention the shot size), export video for submission.
Final Outcome:
Editing Exercise - Lalin:
Storyboard is given by Mr Martin in Google Drive. We just need to
follow the arranged storyboard and arrange and edit all the footage
and graphics.
I downloaded all the footage given by Mr Martin and then imported
into Premiere Pro to start my edit. Firstly, I arranged all the scene
properly and cut them into parts that I want, After that, I added
graphics of dialogue to match with the scene. I then added iPhone sound
effect.
Figure 2.6.3 progress
Before exporting out the video, I added Cross Dissolve in the
beginning and ending part. Also, Cross Dissolve is also added in one
of the scene that taught by Mr Martin in his tutorial video.
Figure 2.6.4 progress
Final Outcome:
Asynchronous Class Materials Questions
Lalin
Figure 2.7 lalin
- Which part is act 1, act 2, act 3 respectively? Describe each act with ONE paragraph only.
Act 1 starts with introducing Lalin. Although she is
an internet idol, she has blemish and acne-prone skin on
her face. She moves to Japan from Thailand. She hides who she really is by using
masks and filters, turning into an online idol. She struggles with an
internal fear of rejection despite her popularity on the internet. She
also starts with an online relationship with a Japanese guy, Nut. This
unexpected situation leads Lalin extremely close to facing her true self
when Nut says he wants to meet in person. Act 2 starts up with Lalin
making video calls to display her relationship with Nut. As Nut's
arrival in Japan, he requests to meet Lalin, but Lalin rejects him.
Lalin doesn't have the courage to face her true self. Act 3 occurs when Lalin finally removes her mask and decides she should accept
her true self. She also realises that she met Nut before after she
opens what Nut gave her.
- What is the inciting incident in the movie?
The inciting incident occurs when Nut and Lalin begin an online
relationship and Nut requests to meet her in person.
- What is the midpoint scene in the movie?
The midpoint scene occurs when Lalin struggles in facing her true
self when Nut requests to meet her face-to-face. She then rejected
Nut.
- What is the Climax scene in the movie?
The climax scene occurs when Lalin finds out she met Nut before.
Nut used to be an obese guy but turns handsome and fit now.
- What is the theme of the movie?
The theme of the movie "Lalin" is about self-acceptance. We must be
confident and accept our true self.
Everything, Everywhere, All at once
Figure 2.8 Everything, Everywhere, All at once
- Which part is act 1, act 2, act 3 respectively? Describe each act with ONE paragraph only.
Act 1 shows Evelyn, the protagonist who struggles with her life as a mother and small business owner. The inciting incident happens when she discovers her ability to access parallel universes, which starts with a series of events that change her everyday routine
and send her on a journey for self- discovery.
Act 2 shows Evelyn discovers how to travel through the multiverse
and meets versions of herself. She learns that Jobu Tupaki, her daughter
Joy's alternate version poses a serious threat to the multiverse. The
turning point comes when Evelyn completely understands the extent of the
multiverse and her own abilities, strengthening her determination to
protect her family and all existence. Act 3 occurs when Evelyn and her
father are fighting. Evelyn reaches out to her daughter with compassion
and understanding, showing her that life is worth living even in a
situation of chaos, which has a happy ending in which Joy and Evelyn are
saved by Evelyn's father.
- What is the inciting incident in the movie?
The inciting incident occurs when Waymond reveals the aspects of
multiverse to Evelyn.
- What is the midpoint scene in the movie?
The midpoint scene occurs when Evelyn finds out Jobu Tupaki, her
daughter Joy's alternate version poses a serious threat to the
multiverse.
- What is the Climax scene in the movie?
The climax scene occurs when Evelyn and her dad are fighting.
- What is the theme of the movie?
The theme of "Everything, Everywhere, All at Once" explores the
transforming power of self-discovery and relationship between family.
Quiz Result:
Figure 2.9 Quiz Result
[back to top]
WEEK 3 TASK
Asynchronous Class Materials Reflection
Storyboard
Storyboard
is a series of ordered drawings, with camera direction, dialogue,
or other pertinent details. It sketches out how a video will
unfold, shot by shot. Storyboard is a tool to help you in
pre-production. Storyboard can include details such as camera angles, character
movements, dialogue, and even notes about special effects or
sound. There are two basic versions of storyboard format, traditional
and thumbnail.
Traditional storyboards are basic pencil sketches that include detailed
information like arrows for camera movement, characters, props and
more. Thumbnail style storyboards don't have any
writing. They’re not used as often as detailed ones.
There are few steps to make storyboards. Firstly, identify key
scenes in the script. Then, give each key scenes a number and a relevant title so it's easy to
link them back to the broader story in the script. Add images and
sketches. Also, describes the style, mood, and behaviour of characters and write out
the details of each scene. Lastly, share with your team and get
feedback from others.
Quiz Result:
Figure 3.3 Quiz Result
[back to top]
WEEK 4 TASK
Asynchronous Class Materials Reflection
Production Stages & Production Crew
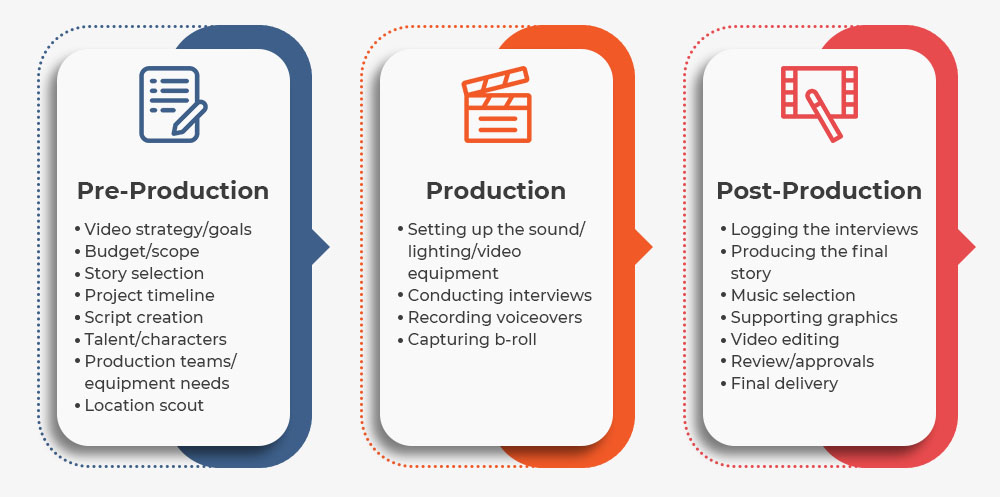
Figure 4.1 Production Stages
Production is sometimes used to refer to one of three
steps in the filmmaking process. People divide up the
filmmaking process into stages.
Pre-production is all the
necessary preparation before making the film,
including writing the script, creating
storyboards, casting actors, scouting locations,
designing sets and costumes and hiring crew
members. Budgeting and getting the team together are necessary in the process of
pre-production. Also, pre-visualising is to plan
how the producer wants the film to look before
starting to film. Next, production happens during
the actual filming. The production team captures
the footages that needed and planned in the
planning session. In post-production, all the
footage is edited with music and sound effects,
colour grading and visual effects. This stage
requires focusing to detail and keen eye for
storytelling.
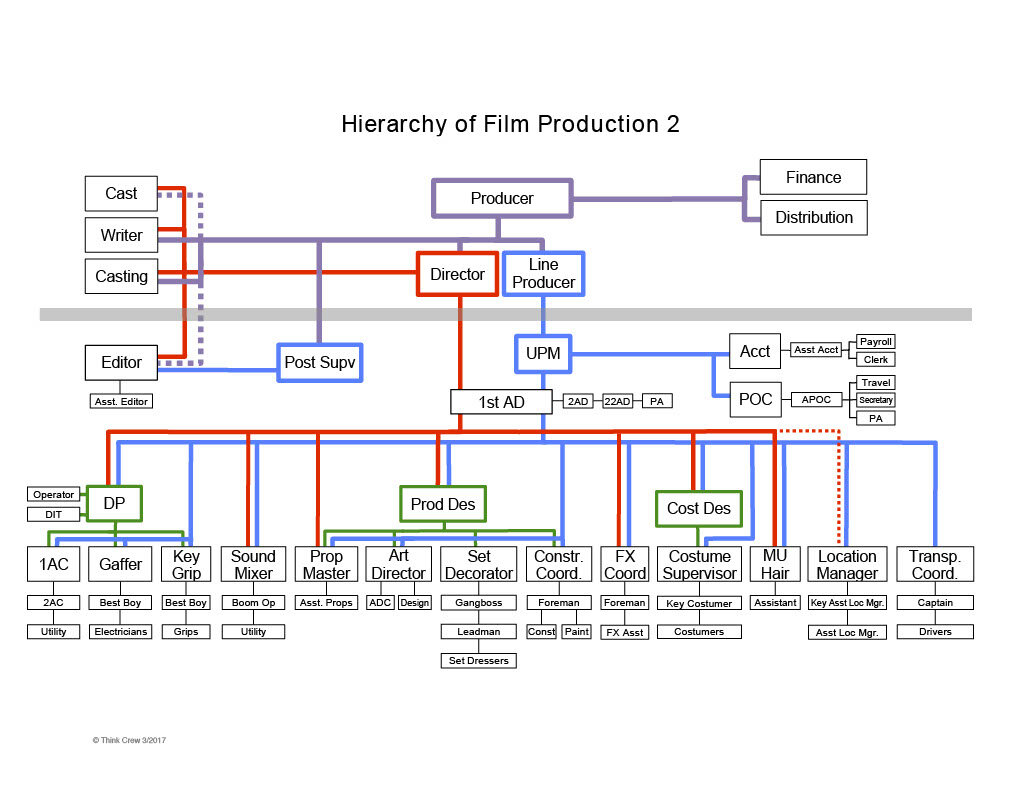
Figure 4.2 Production Stages and Production Crew
Production crew is a team of professionals who work
together to make the film or video a reality. A complete
production crew needs producer, director, cinematographer,
production designer, sound designer and editor. Everyone of
them has specific role and responsibilities. A director
directs the actors' performances and make decisions about
filming out the outcome. Producer casts actors, hires the
crew and needs to ensure that the project is completed on
time and within budget. The cinematographer is also known as
the director of photography. The production designer
work closely with the director and cinematographer to
ensure the visual design of the film looks good.
Sound designer is responsible for the audio aspects of
the film . They record and edit dialogue , sound
effects and music. Lastly, The editor will shape teethe
pacing, tone and structure of the film.
The roles mentioned above are all key production crew
members. There are some other roles on a production crew
too, including grips, gaffers, makeup artists, and stunt coordinators.
Quiz Result:
Production Stages
Figure 4.3 Quiz Result
Production Crew
Figure 4.3 Quiz Result







Comments
Post a Comment